At airports and airlines around the globe, there is an increasing trend of fully end-to-end self-service air travel experience that is biometric oriented technology. Due to the introduction of electronic passports, automated systems and biometrically controlled boarding, the air travel of the future is becoming more and more secure and efficient.
The Self-Service Revolution around Air Travel
Maximization of consumer convenience has been the overarching aim of the majority of airports over the last 20 years, which in large part explains why automated terminals like self check-in kiosks and automated baggage drop off have become common practices at most airports. Such modernizations contributed to average waiting times for passengers standing in line to drop off baggage by an impressive 30%.
Research shows that travelers welcome technology that enhances their travel experience by reducing rough edges. It is this proclivity for machines that makes the airports adopt biometric systems that dispense with the need to physically hold tickets while boarding and stand in queues to have their identity checked.
The Effect of Biometrics on ID Checks
To authenticate an individual, biometric systems use tables of biological markers, including facial features, fingerprints and iris patterns. There is perfect compatibility between this technology and the layout of the airport which increases security and efficiency in terms of passengers being boarded.
Global circulation of e-Passports is over 2.5 billion. The data on these passports includes biometrics data like certain facial features which can be cross referenced via facial recognition software. Moreover, the introduction of eGates automated border control systems eliminates the loopholes and increases the speed of border control crossing.
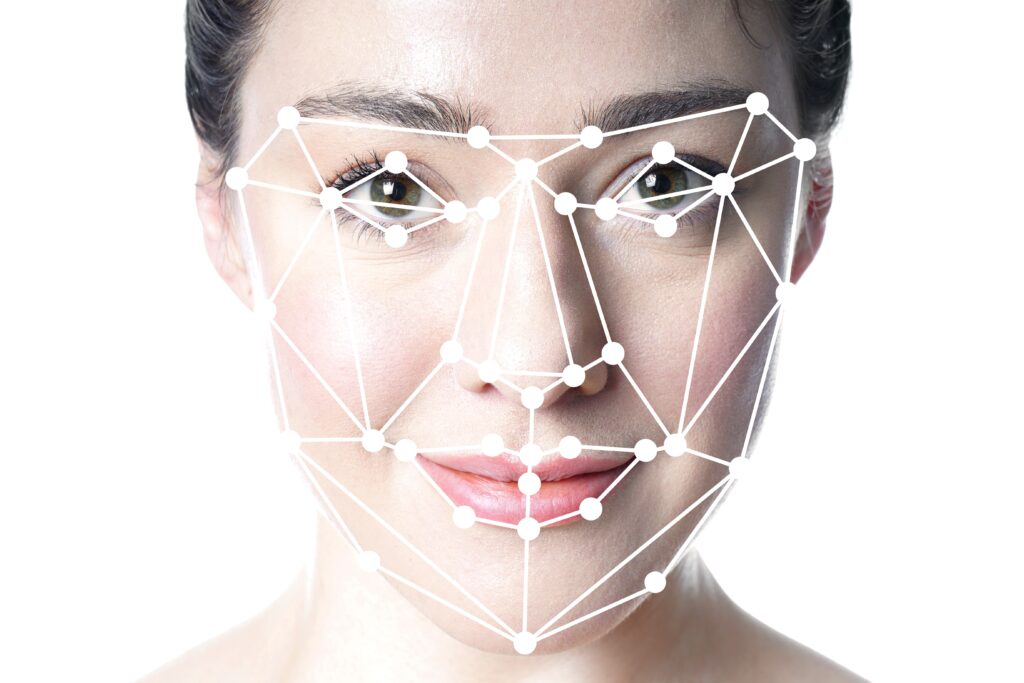

How Biometric Boarding Works
Generally, the biometric boarding process is composed of 3 steps:
Biometric Data Enrollment: Passengers provide airlines or airport systems and sometimes register their biometrics data such as scanning of facial features before using the system for the first time. This data is kept in a safe manner for any future contract that may require this information to be verified.
Identification Verification at the Check-in Counter: At the check-in desk passengers first had their biometric data collected by the system. The data collected is used to compare with the stored images. In case there was a match, it then meant the correct ticketed passenger was checking in. Meaning, security enhanced right there before travel began.
Biometric Recognition at the Gate: Aboard facial recognition cameras, other biometric devices obtain the passengers facial features for verification again and if they perform a cross reference and identify a match, the passenger is then cleared to board as advancing to slow phases of the boarding time eliminating the need to cross check in worst case scenarios. This automated system ensures accuracy and reduction of waiting times ensuring reliable and unified efficient boarding.
How biometrics would change the travel segment
Supplementary Security: The identity of the individual now is replaced with biometric information which is unique. In this way, identity fraud is minimized, and only authorized personnel can board the flights. Then the human factor becomes less of a risk at automated checks.
Operational Efficiency: Automating the boarding process means that the staff to manage the passengers is reduced while the movement of the passengers becomes efficient. This translates boarding time to be up to 80% cut, thus optimizing the airline’s processes.
Improved Experience for the Passengers: A biometric boarding process is fast and contactless, so the passengers find it convenient. Reduced queues and waiting time contribute to the overall satisfaction of the passengers.
Revenue Generation: The faster the passengers go through the check in and boarding process the more time they have to spend at the duty-free outlets and restaurants increasing the revenue of the airport.
Where The Difficulties lie
Many challenges are To be faced with all the advantages that biometric solutions proposed. Three such challenges are:
The Cost And Upkeep: These solutions have had problems with maintenance of their high initial costs as well as regular upgrades.
Privacy Issues: Passengers are likely to withhold biometric information if there are no explicit guidelines on how the data is going to be put into use and how it will be stored.
Again, a technical limitation has many factors including the environment, such as insufficient illumination and the angle of view of the camera that may influence accuracy. For gaining passenger confidence, It’s imperative for airports and airlines to put in place appropriate strategies, adhere to the laws governing data protection, and be transparent.
The Future Starts Today
Biometric boarding and self service systems would not be something new but a modern need with time as ways of traveling abroad evolve. With Europe’s Entry/Exit System (EES) or TSA PreCheck using biometrics innovations: The inspiration for change was clearly stated as “flanding and checks will be things of the past”.
As more airports and airlines fit on these technologies, passengers are sure to have secure, quick and pleasant air travel. With biometric tech, the traveling experience is already altering how we maneuver around the airlines. The aim is to make the whole procedure from check-in through touching down to the selected country as quick as possible.